Introduction
Neurofeedback therapy is an innovative approach that uses real-time displays of brain activity to teach self-regulation of brain function. This technique has gained popularity as a complementary treatment for various psychological and neurological conditions, including Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), anxiety, depression, and more.
By providing feedback on brain activity, neurofeedback empowers individuals to modify their brain patterns, promoting mental well-being and cognitive enhancement. This article explores the mechanisms, benefits, applications, and challenges of neurofeedback therapy, shedding light on its potential to transform mental health treatment.
See also our Trivia game generator or Fun Facts game for even more fun!

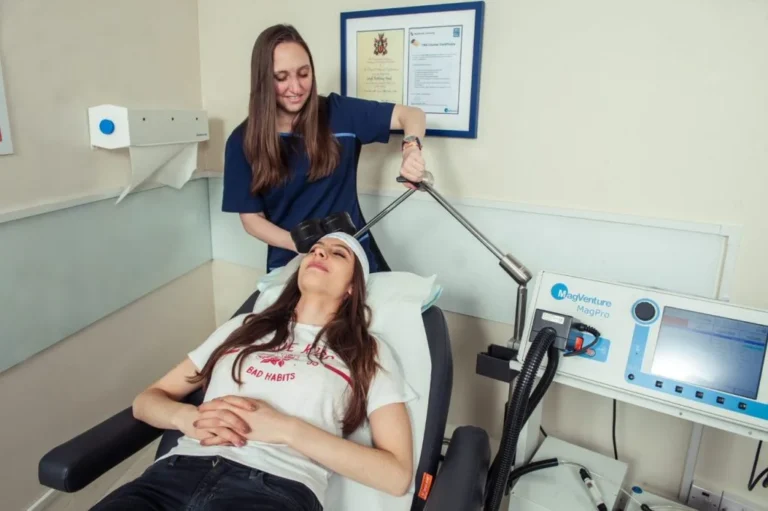
What is Neurofeedback Therapy?
Understanding the Basics of Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback, also known as EEG biofeedback, is a type of biofeedback that provides individuals with information about their brain activity. By using electroencephalography (EEG) to measure brain waves, neurofeedback allows individuals to see their brain activity in real-time and learn how to control it.Key Points:
- Non-invasive: Neurofeedback is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve medication or surgical interventions.
- Real-time feedback: Patients receive immediate feedback on their brain activity through audio or visual signals, enabling them to adjust their mental states accordingly.
- Learning process: Neurofeedback is based on the principle of operant conditioning, where individuals learn to modify their brain activity through reinforcement.
Historical Background
The concept of neurofeedback dates back to the 1960s, with early research demonstrating the possibility of training individuals to control their brain waves. Over the decades, neurofeedback has evolved, gaining recognition as a therapeutic tool for various mental health conditions.
Its applications have expanded beyond ADHD to include anxiety, depression, insomnia, and even performance enhancement in athletes and musicians.
How Does Neurofeedback Work?
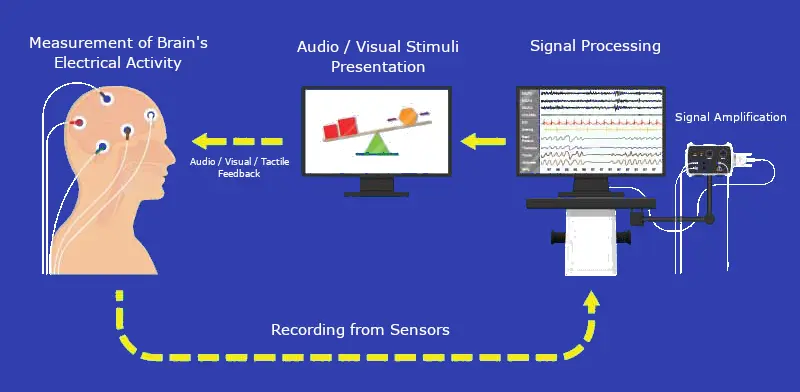
The Science Behind Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback operates by measuring brain activity and providing feedback in real-time. The process typically involves the following steps:
- EEG Measurement: Electrodes are placed on the scalp to record brain wave activity. The EEG data is processed to identify specific brain wave patterns.
- Feedback Mechanism: The processed data is translated into visual or auditory signals, which are presented to the individual. For example, a video game may become easier or harder to play based on the individual’s brain activity.
- Training Sessions: Over multiple sessions, individuals learn to modify their brain wave patterns to achieve desired mental states, such as increased focus or relaxation.
Types of Brain Waves
Neurofeedback focuses on various types of brain waves, each associated with different mental states:
- Delta Waves: Associated with deep sleep and restorative processes.
- Theta Waves: Linked to relaxation, creativity, and meditation.
- Alpha Waves: Related to calmness and alertness, often present during relaxed but focused states.
- Beta Waves: Associated with active thinking, problem-solving, and alertness.
- Gamma Waves: Linked to higher-level cognitive processing and information integration.
By training individuals to enhance or suppress specific brain wave patterns, neurofeedback can promote desired mental states and improve overall cognitive function.
Benefits of Neurofeedback Therapy
Why Consider Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback therapy offers several advantages over traditional treatment methods, making it an appealing option for many individuals:
- Non-invasive and drug-free: Neurofeedback does not involve medications or invasive procedures, making it a safer alternative for those concerned about side effects.
- Personalized treatment: Neurofeedback protocols can be tailored to individual needs, allowing for a customized approach to mental health treatment.
- Long-lasting effects: Many individuals report sustained improvements in symptoms following neurofeedback training, as the skills learned during therapy can be applied in everyday life.
Efficacy in Treating ADHD
Neurofeedback has shown particular promise in treating ADHD. Research indicates that neurofeedback can help individuals with ADHD improve attention, reduce impulsivity, and enhance overall cognitive functioning.
A systematic review published in the Journal of Attention Disorders found that neurofeedback is effective in reducing ADHD symptoms, with many studies reporting significant improvements in attention and behavior.
Additional Applications
Beyond ADHD, neurofeedback therapy has been explored for various conditions, including:
- Anxiety and Depression: Neurofeedback can help regulate emotional responses and improve mood by training individuals to achieve more balanced brain wave patterns.
- Insomnia: By promoting relaxation and reducing hyperarousal, neurofeedback can improve sleep quality and duration.
- Performance Enhancement: Athletes and musicians have used neurofeedback to enhance focus, reduce performance anxiety, and improve overall performance.
Neurofeedback Protocols
Common Neurofeedback Protocols
Neurofeedback therapy employs various protocols, each targeting specific brain wave patterns and mental states. Some common protocols include:
- Theta/Beta Training: This protocol aims to reduce theta waves (associated with inattention) and increase beta waves (linked to focus and alertness). It is often used for ADHD treatment.
- Alpha/Theta Training: This protocol combines alpha and theta training to promote relaxation and creativity. It is commonly used for anxiety and stress management.
- Slow Cortical Potential (SCP) Training: SCP training focuses on regulating slow cortical potentials to improve attention and self-regulation. It has shown promise in treating ADHD and epilepsy.
Individualized Treatment Plans
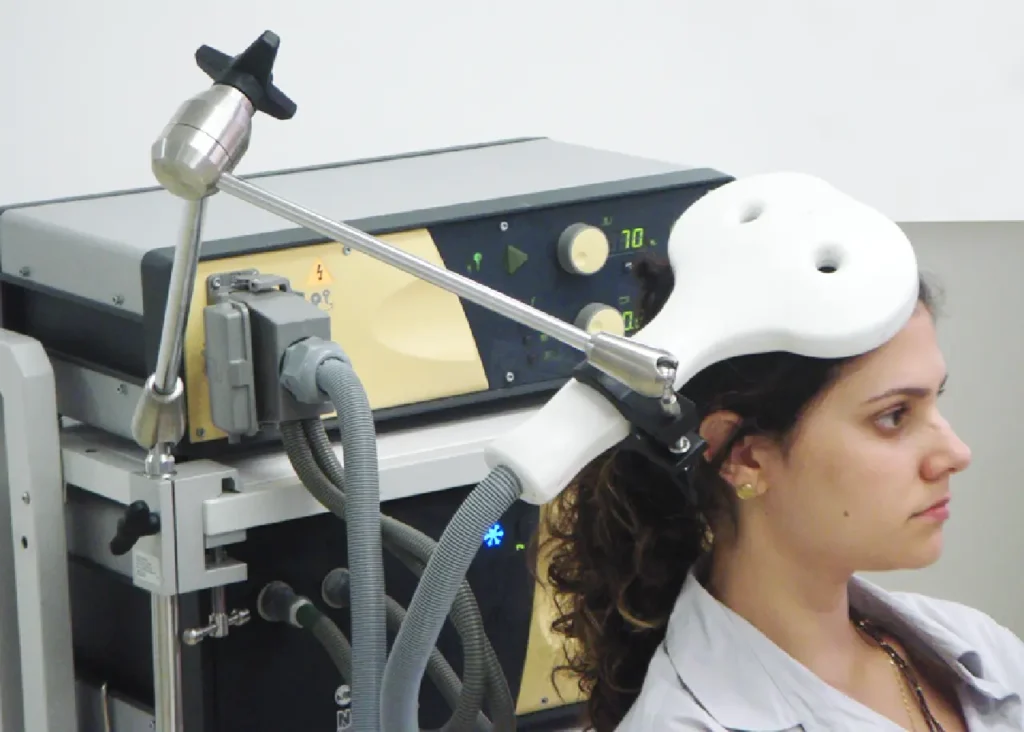

Neurofeedback therapy is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual’s specific needs, taking into account their symptoms, goals, and preferences. A thorough assessment is conducted before starting therapy to determine the most appropriate protocols and training strategies.
Challenges and Considerations
Limitations of Neurofeedback Therapy
While neurofeedback therapy offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges and limitations:
- Mixed Evidence: Despite promising results, the scientific evidence supporting neurofeedback’s efficacy remains mixed. Some studies report significant improvements, while others fail to demonstrate consistent results.
- Time and Cost: Neurofeedback therapy often requires multiple sessions over an extended period, which can be time-consuming and costly for patients.
- Individual Variability: The effectiveness of neurofeedback can vary significantly among individuals, with some experiencing substantial improvements while others see little to no change.
Ethical Considerations
As with any therapeutic intervention, ethical considerations are essential in neurofeedback therapy. Practitioners must ensure that patients are fully informed about the potential benefits and limitations of the treatment, as well as any associated risks. Additionally, the use of neurofeedback for performance enhancement in non-clinical populations raises ethical questions regarding fairness and access.
The Future of Neurofeedback Therapy
Emerging Trends and Research Directions
As research continues, the future of neurofeedback therapy looks promising. Emerging trends and areas of exploration include:
- Integration with Other Therapies: Combining neurofeedback with other therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness practices, may enhance treatment outcomes.
- Advancements in Technology: Innovations in neurofeedback technology, such as mobile applications and wearable devices, may make neurofeedback more accessible and user-friendly.
- Longitudinal Studies: More long-term studies are needed to assess the durability of neurofeedback effects and its potential for various populations.
Research Directions
Future research will likely focus on optimizing neurofeedback protocols, exploring its efficacy in diverse populations, and investigating the underlying mechanisms of action. Understanding how neurofeedback influences brain function and behavior will be crucial for refining treatment approaches and maximizing benefits.
Conclusion
Neurofeedback therapy represents a significant advancement in the field of mental health treatment. By providing individuals with the tools to self-regulate their brain activity, neurofeedback has the potential to improve cognitive functioning, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. While challenges and limitations exist, ongoing research and advancements in technology may pave the way for more effective and accessible neurofeedback interventions. As awareness of neurofeedback grows, it may become an integral part of comprehensive mental health care, offering hope and healing to those in need.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is neurofeedback therapy?
Neurofeedback therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses real-time displays of brain activity to teach individuals how to self-regulate their brain function.
How does neurofeedback work?
Neurofeedback works by measuring brain activity through EEG, providing feedback in real-time, and allowing individuals to learn how to control their brain waves.
What conditions can neurofeedback treat?
Neurofeedback is commonly used to treat ADHD, anxiety, depression, insomnia, and for performance enhancement in athletes and musicians.
Is neurofeedback safe?
Neurofeedback is generally considered safe, with minimal side effects. However, individuals should consult with a qualified practitioner before starting therapy.
How long does neurofeedback therapy take?
Neurofeedback therapy typically requires multiple sessions over several weeks, with each session lasting about 30 to 60 minutes.
Can neurofeedback be combined with other therapies?
Yes, neurofeedback can be integrated with other therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness practices, to enhance treatment outcomes.
How effective is neurofeedback for ADHD?
Research indicates that neurofeedback can be effective in reducing ADHD symptoms, with many studies reporting significant improvements in attention and behavior.
Are results from neurofeedback therapy long-lasting?
While many individuals report sustained improvements, the durability of neurofeedback effects can vary among individuals and may require ongoing practice.
What should I expect during a neurofeedback session?
During a neurofeedback session, electrodes will be placed on your scalp to measure brain activity, and you will receive feedback through visual or auditory cues as you learn to regulate your brain waves.
How do I find a neurofeedback provider?
You can search online directories or consult with your healthcare provider for recommendations on qualified neurofeedback practitioners in your area.
Reference
- Neurofeedback: A Comprehensive Review on System Design and Clinical Applications – NCBI
- What Is Neurofeedback Therapy Used For? – Drake Institute
- How Does Neurofeedback Therapy Help Improve Brain Function?
- Neurofeedback Orem and Draper, Utah | Aspen Valley Wellness
- Clinical efficacy of neurofeedback protocols in treatment of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): A systematic review
- Neurofeedback Therapy: Can It Effectively Treat ADHD? – ADDitude