Introduction
Brain scans, or neuroimaging, have become increasingly important in the field of psychiatry as researchers and clinicians seek to understand the complex relationship between brain structure, function, and mental health disorders.
\While traditional diagnostic methods primarily rely on clinical assessments and patient history, advances in neuroimaging technology have opened new avenues for diagnosing and treating mental illnesses.
This article explores the role of brain scans in mental health, their types, applications, limitations, and future directions in research. As mental health disorders continue to rise globally, the integration of neuroimaging into clinical practice offers the potential for more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans.
Understanding how brain scans can aid in the evaluation of mental illness is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Stay Sharp with our Trivia game generator or Fun Facts game for you mental exercises and mental sharpness!
What Are Brain Scans?
Understanding Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging refers to a variety of techniques used to visualize the structure and function of the brain. These techniques can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Structural Imaging: Provides detailed images of the brain’s anatomy, allowing for the identification of physical abnormalities such as tumors, lesions, or structural changes associated with mental illness.
- Functional Imaging: Measures brain activity by assessing changes in blood flow, metabolism, or electrical activity. This type of imaging helps researchers understand how different brain regions interact during cognitive processes and emotional responses.
Common Types of Brain Scans
| Type of Brain Scan | Description | Uses in Mental Health |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Uses strong magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of brain structures. | Identifying structural abnormalities, such as lesions or atrophy in conditions like schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Computed Tomography (CT) Scan | Combines X-ray images to create cross-sectional images of the brain. | Assessing brain injuries, tumors, or hemorrhages that may contribute to mental health symptoms. |
| Positron Emission Tomography (PET) | Measures metabolic activity in the brain by injecting a radioactive tracer. | Evaluating brain function and neurotransmitter activity in disorders like depression and anxiety. |
| Functional MRI (fMRI) | Measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow during specific tasks or rest. | Understanding brain activity patterns associated with cognitive tasks, emotional processing, and mental health disorders. |
| Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) | Similar to PET, but uses different tracers to assess blood flow and activity in the brain. | Identifying areas of hypo- or hyperactivity in conditions like ADHD and depression. |
The Role of Brain Scans in Diagnosing Mental Illness

Diagnostic Utility
While brain scans can provide valuable information about the brain’s structure and function, they are not standalone diagnostic tools for mental illness. Instead, they are typically used in conjunction with clinical assessments to rule out organic causes of symptoms or to support a diagnosis.Key Points:
- Ruling Out Other Conditions: Brain scans can help identify medical conditions that may mimic or exacerbate mental health symptoms, such as tumors, strokes, or infections.
- Research Applications: Neuroimaging studies contribute to the understanding of the neurobiological underpinnings of mental disorders and help identify biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment response.
Current Limitations
Despite advancements in neuroimaging technology, there are limitations to its use in diagnosing mental illness:
- Lack of Specificity: Brain scans cannot definitively diagnose mental health disorders on their own. For example, structural changes in the brain may be present in multiple disorders, making it difficult to pinpoint a specific diagnosis.
- Need for Large Sample Sizes: Many neuroimaging studies have relied on small sample sizes, which can lead to unreliable results. Larger, more diverse studies are needed to establish robust correlations between brain imaging findings and specific mental health conditions.
“Brain scans can provide valuable insights into the underlying biology of mental health disorders, but they should be used as part of a comprehensive assessment rather than as a sole diagnostic tool.” – Psychiatrist
Applications of Brain Scans in Mental Health Research
Understanding Mental Disorders
Neuroimaging studies have revealed important findings related to various mental health disorders, contributing to our understanding of their neurobiological basis. Some notable findings include:
- Depression: Research has shown that individuals with major depressive disorder may exhibit reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex and increased activity in the amygdala, which are associated with mood regulation and emotional processing.
- Schizophrenia: Studies have identified structural abnormalities, such as enlarged ventricles and reduced gray matter volume in specific brain regions, in individuals with schizophrenia.
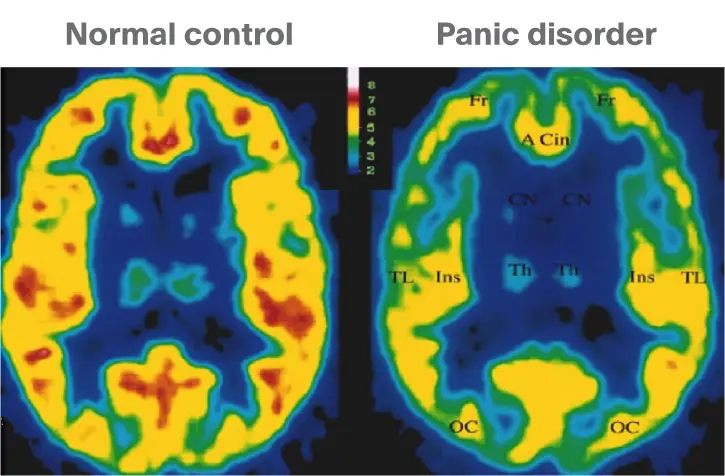
- Anxiety Disorders: Neuroimaging studies have indicated hyperactivity in the amygdala and altered connectivity between brain regions involved in fear and anxiety processing.
Predicting Treatment Outcomes
Brain scans can also play a role in predicting treatment outcomes for individuals with mental health disorders. For example:
- Response to Antidepressants: Structural MRI scans have shown promise in predicting treatment response to antidepressants, with some studies reporting up to 89% accuracy in predicting outcomes based on brain structure.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Functional MRI studies have indicated that changes in brain activity patterns during CBT can be associated with symptom improvement, suggesting that neuroimaging may help tailor treatment approaches.
Future Directions in Neuroimaging Research
The field of neuroimaging continues to evolve, with ongoing research focused on enhancing the diagnostic utility of brain scans and identifying biomarkers for mental health disorders. Some promising areas of exploration include:
- Machine Learning and AI: The integration of machine learning algorithms with neuroimaging data has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and predict treatment responses by identifying patterns that may not be apparent through traditional analysis.
- Longitudinal Studies: Conducting long-term studies that track changes in brain structure and function over time can provide valuable insights into the progression of mental health disorders and the effects of treatment.
- Diversity in Research: Ensuring that neuroimaging studies include diverse populations will enhance the generalizability of findings and improve our understanding of how mental health disorders manifest across different demographics.
Conclusion
Brain scans, or neuroimaging, have become an essential tool in the field of psychiatry, providing valuable insights into the structure and function of the brain in relation to mental health disorders. While they are not standalone diagnostic tools, brain scans can help rule out organic causes of symptoms and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of mental illness.
As research continues to advance, the integration of neuroimaging into clinical practice may lead to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans for individuals with mental health disorders. By leveraging the power of brain scans, healthcare providers can enhance their understanding of mental health and improve outcomes for patients.
Individuals seeking answers about their mental health, discussing the potential role of brain scans with a qualified healthcare provider can be an important step in the journey toward understanding and managing their condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are brain scans used for in mental health?
Brain scans are used to visualize the structure and function of the brain, helping to identify underlying conditions that may contribute to mental health symptoms and supporting the diagnosis of certain disorders.
Can brain scans diagnose mental illness?
No, brain scans cannot diagnose mental illness on their own. They are typically used in conjunction with clinical assessments to rule out organic causes of symptoms and to support a diagnosis.
What types of brain scans are commonly used in mental health?
Common types of brain scans used in mental health include MRI, CT scans, PET scans, fMRI, and SPECT.
How do brain scans help in understanding mental disorders?
Neuroimaging studies have revealed structural and functional abnormalities associated with various mental disorders, contributing to our understanding of their neurobiological basis.
Are there any risks associated with brain scans?
While brain scans are generally considered safe, some types of scans, such as those involving radiation, may pose risks. It’s essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
How can brain scans predict treatment outcomes?
Some studies have shown that brain scans can help predict treatment responses to medications and therapies by identifying specific brain patterns associated with improvement.
What is the future of neuroimaging in mental health?
The future of neuroimaging in mental health includes advancements in machine learning, longitudinal studies, and a focus on diversity to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
Can brain scans be used for research purposes?
Yes, brain scans are widely used in research to study the neurobiological underpinnings of mental health disorders and to identify potential biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment.
How can I find a provider for brain imaging?
Consult with your primary care physician or mental health provider for referrals to facilities that offer neuroimaging services.
Is neuroimaging a standard part of mental health evaluations?
Neuroimaging is not typically a standard part of mental health evaluations but may be recommended in specific cases to rule out other medical conditions or support a diagnosis.
References
- Choosing Therapy. (2023). How Are Brain Scans Used to Diagnose Mental Illness? https://www.choosingtherapy.com/brain-scan-for-mental-illness/
- National Institutes of Health. (2019). Neuroimaging and Mental Illness: A Window Into the Brain. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GOVPUB-HE20-PURL-LPS125935/pdf/GOVPUB-HE20-PURL-LPS125935.pdf
- NPR. (2022). Brain scans may reveal a lot about mental illness, but not until studies get bigger. https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2022/04/26/1094319294/mri-brain-scan-mental-illness-brain-research
- Falkai, P., Schmitt, A., & Andreasen, N. (2019). Forty years of structural brain imaging in mental disorders: is it clinically useful or not? Psychological Medicine, 49(11), 1741-1751. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6296397/
- Amen Clinics. (2024). Brain SPECT | Brain Scan. https://www.amenclinics.com/services/brain-spect/