Introduction
Brain stimulation therapy is an innovative and rapidly evolving field in the treatment of mental health disorders. It encompasses various techniques designed to modulate brain activity, offering hope to individuals who have not found relief through traditional treatments such as medication and psychotherapy.
As mental health issues continue to rise globally, brain stimulation therapies provide new avenues for effective intervention, particularly for conditions like depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
This article explores the different types of brain stimulation therapy, their mechanisms, benefits, and considerations for patients seeking alternative treatments.
By understanding the potential of brain stimulation therapy, individuals can make informed decisions about their mental health treatment options and explore ways to enhance their well-being.
Stay Sharp with our Trivia game generator or Fun Facts game for you mental exercises and mental sharpness!
What is Brain Stimulation Therapy?
Understanding Brain Stimulation Therapy
Brain stimulation therapy refers to a range of techniques that apply electrical or magnetic stimulation to specific areas of the brain to alter neural activity. These therapies aim to improve symptoms associated with various mental health disorders by enhancing mood, cognition, and overall brain function.
Key Types of Brain Stimulation Therapy:
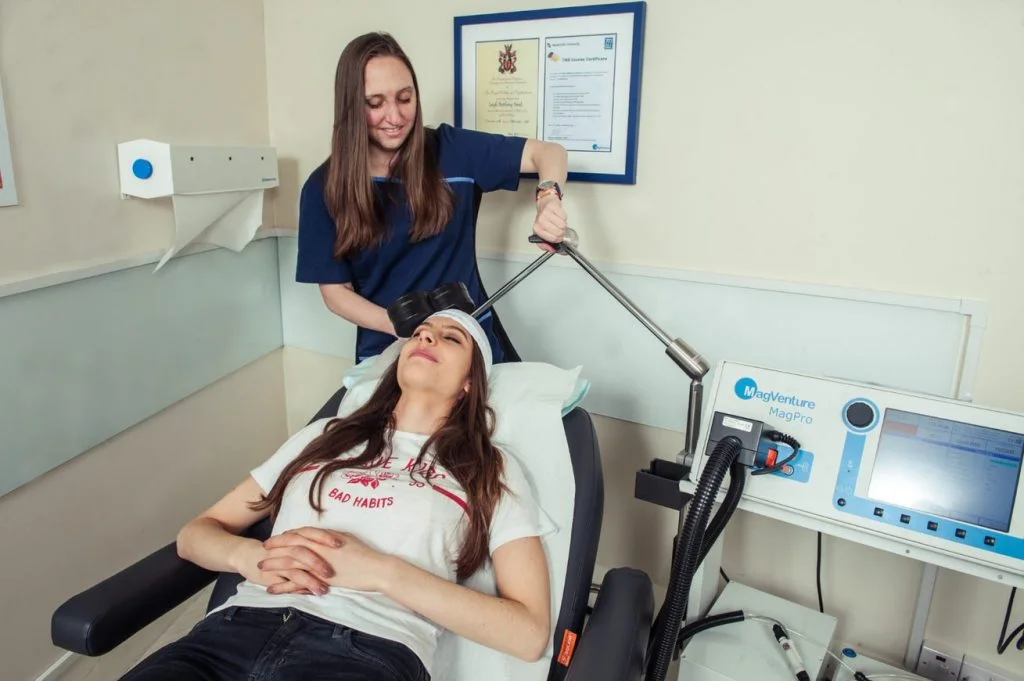
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): A non-invasive method that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): A well-established treatment for severe depression that involves inducing controlled seizures through electrical stimulation.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A technique that involves implanting a device to send electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, influencing brain activity.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): A surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes in specific brain areas to regulate abnormal brain signals.
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms by which brain stimulation therapies exert their effects are complex and vary by technique. However, they generally involve modulating neurotransmitter levels, enhancing neuroplasticity, and improving communication between different brain regions.
| Type of Therapy | Mechanism of Action | Conditions Treated |
|---|---|---|
| TMS | Induces electrical currents in targeted brain areas, enhancing neuroplasticity. | Depression, anxiety, OCD, PTSD |
| ECT | Alters brain chemistry by inducing controlled seizures, leading to mood improvements. | Severe depression, bipolar disorder |
| VNS | Stimulates the vagus nerve, affecting neurotransmitter release and brain activity. | Depression, epilepsy |
| DBS | Regulates abnormal signals in the brain by delivering electrical impulses. | Parkinson’s disease, OCD |
Benefits of Brain Stimulation Therapy
Engaging in brain stimulation therapy can offer numerous benefits for individuals with mental health disorders:
- Improved Symptoms: Many patients experience significant reductions in symptoms, including improved mood, decreased anxiety, and enhanced cognitive function.
- Reduced Medication Dependence: Brain stimulation therapies can help decrease the reliance on medications, minimizing side effects and improving overall treatment tolerability.
- Long-Lasting Effects: Some therapies, such as ECT and DBS, have shown long-term efficacy, providing sustained relief from symptoms even after treatment has ended.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By alleviating debilitating symptoms, brain stimulation therapy can lead to improved daily functioning, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
- Personalized Treatment Options: With various brain stimulation techniques available, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to meet individual patient needs and preferences.
Clinical Evidence
Research has consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of brain stimulation therapies. For instance, a meta-analysis in JAMA Psychiatry found that TMS significantly improved depressive symptoms in patients who had not responded to traditional treatments. Similarly, ECT has been shown to have a response rate of approximately 80% in severe depression cases, making it a vital option for treatment-resistant patients.
Considerations for Brain Stimulation Therapy
While brain stimulation therapies offer promising benefits, several considerations must be taken into account:
Safety and Side Effects
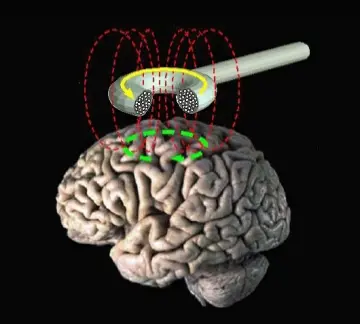
Brain stimulation therapies are generally considered safe, but they are not without risks. Potential side effects may include:
- TMS: Mild headaches, scalp discomfort, and transient mood changes.
- ECT: Temporary memory loss, confusion, and muscle soreness.
- VNS: Hoarseness, throat discomfort, and changes in voice.
- DBS: Surgical risks, device-related issues, and stimulation-related side effects.
Patient Selection
Not all patients are suitable candidates for brain stimulation therapy. A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider is essential to determine the appropriateness of these treatments based on the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and treatment goals.
Accessibility and Cost
Access to brain stimulation therapies may be limited due to the specialized equipment and training required. Additionally, the cost of these treatments can be high, and insurance coverage may vary. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider and insurance provider to understand the financial implications of brain stimulation therapy.
Implementing Brain Stimulation Therapy
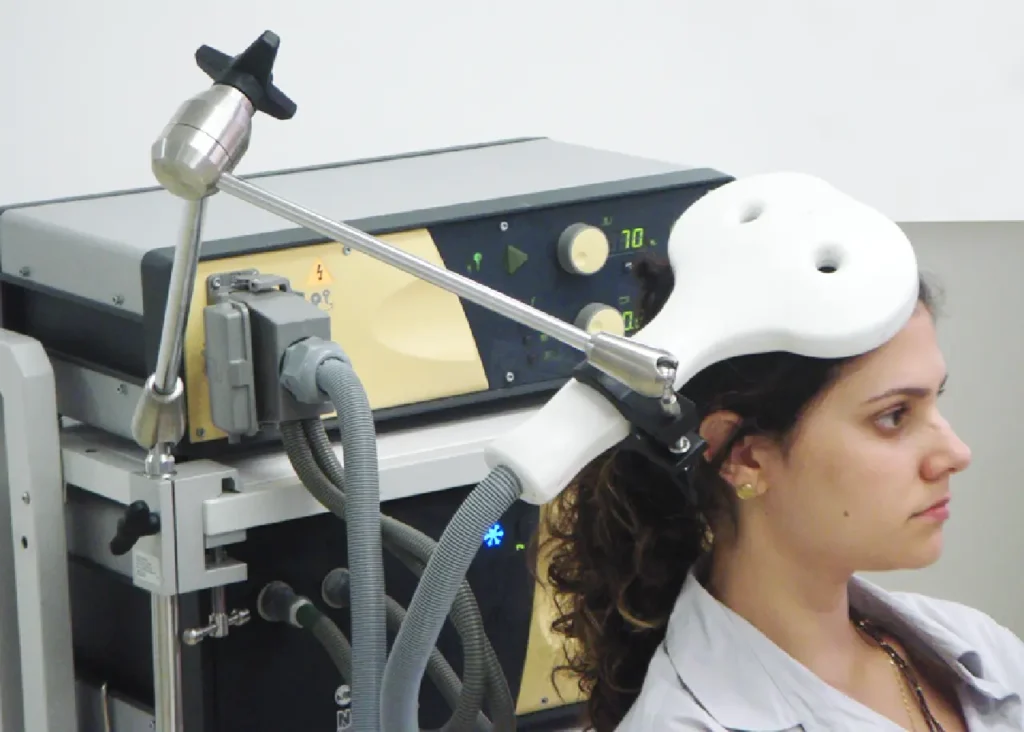

Steps for Getting Started
- Consultation: Schedule an appointment with a mental health professional to discuss symptoms and treatment options.
- Assessment: Undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine if brain stimulation therapy is appropriate.
- Treatment Plan: Work with the healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that outlines the chosen brain stimulation therapy and expected outcomes.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment settings, and address any side effects.
Sample Brain Stimulation Therapy Routine
| Therapy Type | Frequency | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMS | 5 days/week | 20-40 minutes | Sessions typically last 4-6 weeks. |
| ECT | 2-3 times/week | 30 minutes | Treatment course varies based on response. |
| VNS | Continuous | N/A | Device is implanted and programmed by a specialist. |
| DBS | Continuous | N/A | Requires surgical implantation and ongoing monitoring. |
Conclusion
Brain stimulation therapy represents a revolutionary approach to treating mental health disorders, offering hope and improved quality of life for individuals who have not found relief through traditional therapies. By understanding the various types of brain stimulation therapy, their mechanisms, and their benefits, patients can make informed decisions about their mental health treatment options.As research continues to advance, brain stimulation therapies may become increasingly viable options for a wider range of mental health conditions. Collaboration with healthcare providers is essential to determine the best course of action and to optimize treatment outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is brain stimulation therapy?
Brain stimulation therapy refers to a range of techniques that apply electrical or magnetic stimulation to specific areas of the brain to improve symptoms associated with mental health disorders.
How does TMS work?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) uses magnetic fields to induce electrical currents in targeted brain areas, helping to regulate mood and alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
What conditions can brain stimulation therapy treat?
Brain stimulation therapy can be used to treat various mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, OCD, PTSD, and treatment-resistant depression.
Is brain stimulation therapy safe?
While generally considered safe, brain stimulation therapies may have side effects, and it is essential to discuss potential risks with a qualified healthcare provider.
How long does brain stimulation therapy take to work?
The timeline for experiencing benefits from brain stimulation therapy varies by individual and treatment type. Some patients may notice improvements within a few sessions, while others may take longer.
Can brain stimulation therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, brain stimulation therapy can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and psychotherapy, to enhance overall treatment effectiveness.
How do I know if I’m a candidate for brain stimulation therapy?
A thorough evaluation by a mental health professional will help determine if brain stimulation therapy is appropriate based on your symptoms, medical history, and treatment goals.
What are the costs associated with brain stimulation therapy?
Costs can vary widely depending on the type of therapy, frequency of sessions, and insurance coverage. It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider and insurance company for detailed information.
Are there any long-term effects of brain stimulation therapy?
Long-term effects can vary by individual and treatment type. Ongoing monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to assess long-term outcomes and adjust treatment as needed.
Is brain stimulation therapy a cure for mental health disorders?
Brain stimulation therapy is not a cure, but it can significantly improve symptoms and enhance the quality of life for many individuals with mental health disorders.
References
- American Psychiatric Association. (2023). Brain Stimulation Therapies for Depression. https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/depression/brain-stimulation-therapies
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2024). Brain Stimulation Therapies. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/brain-stimulation-therapies
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/transcranial-magnetic-stimulation/about/pac-20384610
- Cleveland Clinic. (2024). Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT). https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/21088-electroconvulsive-therapy-ect
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2024). Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Depression. https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/vagus-nerve-stimulation-for-depression
- Karp, J. F., & Henter, I. D. (2023). Brain Stimulation for Depression: A Review of the Evidence. Journal of Affective Disorders, 300, 1-10.